Tutorial - Holoscan SDK
The Holoscan SDK is part of NVIDIA Holoscan , the AI sensor processing platform that combines hardware systems for low-latency sensor and network connectivity, optimized libraries for data processing and AI, and core microservices to run streaming, imaging, and other applications, from embedded to edge to cloud.
Holoscan SDK - Core Concepts
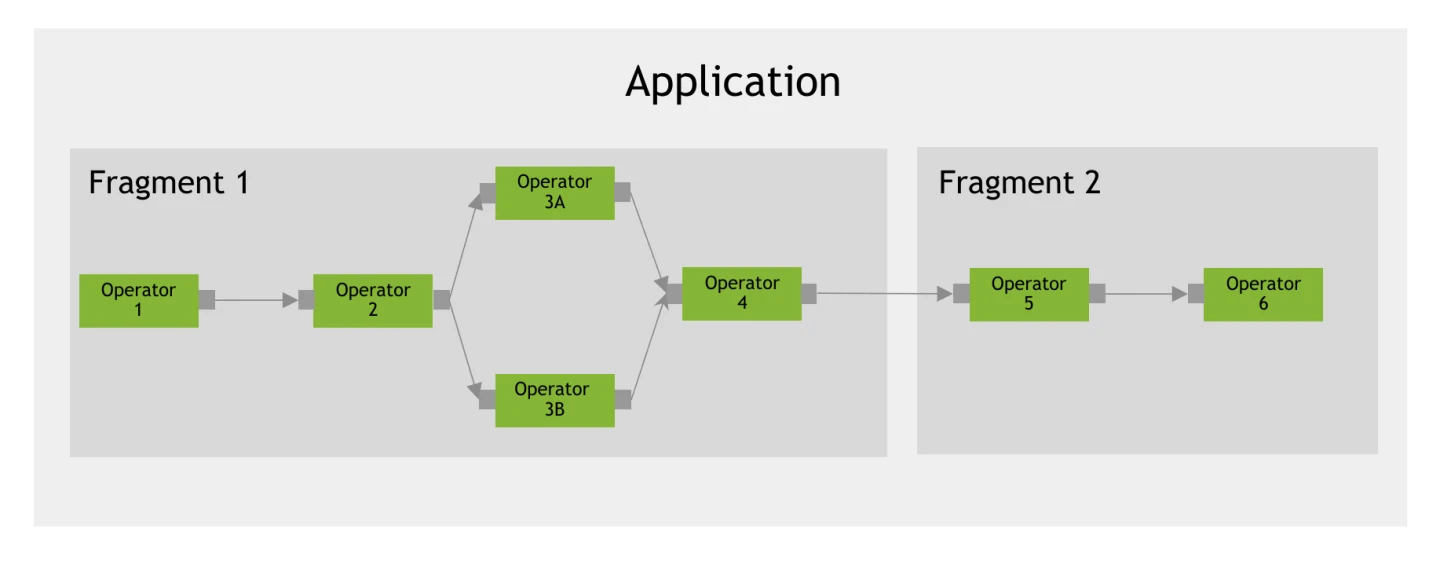
A Holoscan SDK
Application
is composed of
Fragments
, each of which runs a graph of
Operators
. The implementation of that graph is sometimes referred to as a pipeline or workflow, which can be visualized below:
Holoscan SDK - Getting Started on Jetson
The best place to get started using the Holoscan SDK is the HoloHub repo. This is a central repository for the NVIDIA Holoscan AI sensor processing community to share apps and extensions.
So, let's walk through how to run the Surgical Tool Tracking example application from HoloHub!
What you need
-
One of the following Jetson devices:
Jetson AGX Orin (64GB) Jetson AGX Orin (32GB) Jetson Orin NX (16GB) Jetson Orin Nano (8GB)
-
Running one of the following versions of JetPack :
JetPack 6 (L4T r36.x)
-
NVMe SSD highly recommended for storage speed and space
-
13.7 GBforefficientvitcontainer image -
850 Mbfor Tool Tracking ONNX model + example video
-
-
Clone and setup
jetson-containers:git clone https://github.com/dusty-nv/jetson-containers bash jetson-containers/install.sh
Launching a Holoscan-compatible Container
Use the
jetson-containers run
and
autotag
commands to automatically pull or build the Holoscan container.
Use the
-voption to mount HoloHub's./buildand./datadirectories to the local Holoscan package directory so builds and data are cached across runs
jetson-containers run \
-v ./packages/holoscan/holohub/data:/opt/nvidia/holohub/data \
-v ./packages/holoscan/holohub/build:/opt/nvidia/holohub/build \
$(autotag holoscan)
Running HoloHub's Endoscopy Tool Tracking App
An example application from HoloHub is the Endoscopy Tool Tracking application. This sample application demonstrates how the Holoscan SDK can be used to build an efficient pipeline that streams a video feed, preprocesses the data, runs inference using TensorRT, post-processes the data, and renders the video feed with the inference overlays.
![]()
Building The App
The Holoscan SDK uses CMake to build C++ applications and also leverages CMake to pull and build app dependencies. So, regardless of whether an application is implemented using C++ or Python, many apps will still require that you "build" them first.
The Endoscopy Tool Tracking App has both a Python and C++ implementation. Building this app creates the C++ application program, pulls in an example video, and builds the TensorRT engine used for inference.
Go to the HoloHub directory
cd /opt/nvidia/holohub
./run build endoscopy_tool_tracking
Running The Python App
First, add the Holoscan SDK and the HoloHub build directory to your PYTHONPATH environment variable.
export HOLOHUB_BUILD_PATH=/opt/nvidia/holohub/build/endoscopy_tool_tracking
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:$HOLOHUB_BUILD_PATH/python/lib:/opt/nvidia/holoscan/python/lib
python3 /opt/nvidia/holohub/applications/endoscopy_tool_tracking/python/endoscopy_tool_tracking.python --data /opt/nvidia/holohub/data/endoscopy/
Shortly after launching the application, you will see the HoloViz window that visualizes the sample video and the model's outputs:
![]()
Running The C++ App
The C++ app can be run using the run script by specifying the app name:
./run launch endoscopy_tool_tracking
Next Steps
Congratulations! You've successfully run a Holoscan SDK application!
To dive deeper into the Holoscan SDK, explore the SDK's documentation on Core Concepts , Holoscan by Example , and Creating an Application .